✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 11305
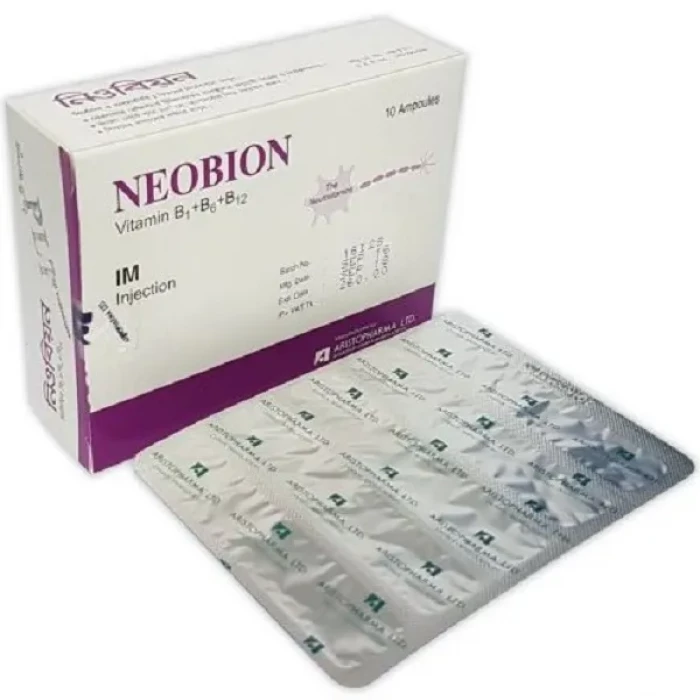
Neobion Vanilla Flavored Neurovitamins 1 Strip
Treatment for vitamin B1, B6, and B12 deficiency syndrome includes vitamin B1, B6, and B12. Additionally, it is indicated for the supportive management of neuritis & non-inflammatory diseases of the nerves, such as
- Diabetic nerve damage
- Periventricular neuralgia
- Lumbago
- Myalgia
- Sciatica, facial neuralgia, and optic neuritis
- An intercostal ache
- Back pain.
Discount
Price: ৳ 114
MRP:
৳
120
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
-
Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
-
Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৭৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে- Google Play Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
- Apple Store থেকে ডাউনলোড
🌙 রমযান অফার 🌙
📲 মোবাইল অ্যাপ অর্ডারে সাশ্রয় বেশী
✅ Description:
- Neobion Tablet is a multivitamin supplement that contains Vitamin B1 (Thiamine), Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), and Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) as its main ingredients. These vitamins are essential for several functions in the body, including the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) helps in the conversion of carbohydrates into energy, as well as the proper functioning of the nervous system. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health and muscle tone.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) is involved in over 100 enzymatic reactions in the body, including the metabolism of amino acids and the synthesis of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. It also supports immune function, red blood cell formation, and hormone regulation.
- Vitamin B12 (Cyanocobalamin) is necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system and the production of red blood cells. It also plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fatty acids and the synthesis of DNA.
- Together, these vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Neobion tablet is often recommended for people who have a deficiency in these vitamins, such as those with poor dietary habits, alcoholics, or elderly individuals. However, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
✔️ Pharmacology
Vitamin B1 helps to maintain healthy neurons, lifts the spirits, and fortifies the heart in addition to converting carbs, fatty acids, and amino acids into energy. Vitamin B6 aids in the production of red blood cells (RBCs), proteins, and neurotransmitters like serotonin, the release of stored energy, the prevention of CVS illnesses and stroke, the reduction of depression, and the relief of insomnia. Vitamin B12 lowers the risk of heart illnesses, protects against anemia, helps to avoid depression, is crucial for RBC formation, and is needed for cell replication. It also lessens nerve discomfort, numbness, and tingling. Vitamin components are effectively absorbed when taken orally. Breast milk contains it, and it is broadly disseminated to most tissues. Thiamine is mostly present in the cell as diphosphate. Thiamine is not much retained in the body, and excess levels are either eliminated in the urine as unaltered thiamine or as metabolites. Following oral administration of pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine, the GIT rapidly absorbs them and converts them to the active forms of pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxamine phosphate. They are mostly stored in the liver, where they are oxidized to 4-pyridoxal acid and other inactive metabolites that are eliminated by urination. Greater amounts of the dosage are excreted unaltered in the urine proportionately when the dose is increased.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Neobion Tablet
- Tablet: 1-3 Tablets per day or as advised by the physician.
Use in children:
- There is no information on the use of this drug in children.
✔️ Overdose Effects of Neobion Tablet
No overdosage symptoms are to be expected in the recommended dosage. If there is a known overdose then treatment is symptomatic & supportive.
✔️ Interactions
No interaction is found
✔️ Contraindications
Vitamin B1, Vitamin B6, and Vitamin B12 are contraindicated in patients on levodopa therapy, and in patients with hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients of the preparation.
✔️ Side Effects of Neobion Tablet
Generally well tolerated but allergic reactions may be observed in a few cases.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Oral tablet form is recommended but due to the presence of benzyl alcohol, injection is not recommended during pregnancy & lactation.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Cyanocobalamin should not be given in patients with subacute degeneration of the spinal cord. Cyanocobalamin is not a suitable to form of vitamin B12 for the treatment of optic neuropathies associated with raised plasma concentrations of cyanocobalamin.
✔️ Storage Conditions
Keep out of reach of children. Store in a cool (below 25°C temperature) and dry place, protected from light.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.